Introduction to BMI Calculator
Definition of BMI Calculator
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used metric for assessing an individual’s body weight relative to their height. It provides a simple numerical value that helps classify people into weight categories such as underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obesity. It is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters.
Historical Context of BMI Development
The concept of BMI Calculator was first introduced in the early 19th century by Adolphe Quetelet, a Belgian mathematician and statistician. Initially called the Quetelet Index, BMI Calculator was primarily used for population studies rather than individual health assessments. Over the years, it has become an essential tool in modern medicine for its simplicity and effectiveness.
How to use BMI Calculater
The BMI Calculator Formula
BMI Calculator is calculated using the formula:
BMI=Weight (kg)Height (m)2BMI = \frac{\text{Weight (kg)}}{\text{Height (m)}^2}BMI=Height (m)2Weight (kg)
For example, if you weigh 70 kg and are 1.75 meters tall, your BMI would be:
BMI=701.752≈22.86BMI = \frac{70}{1.75^2} \approx 22.86BMI=1.75270≈22.86
Units of Measurement in BMI Calculator
For those using pounds and inches, the formula changes slightly:
BMI=Weight (lbs)Height (in)2×703BMI = \frac{\text{Weight (lbs)}}{\text{Height (in)}^2} \times 703BMI=Height (in)2Weight (lbs)×703
This adjustment ensures consistent results across different measurement systems.
Read More : How to lose weight fast
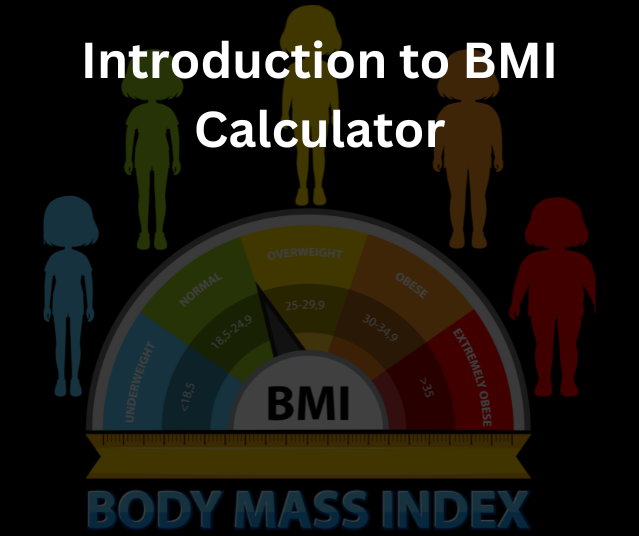
BMI Calculator Categories and Their Significance
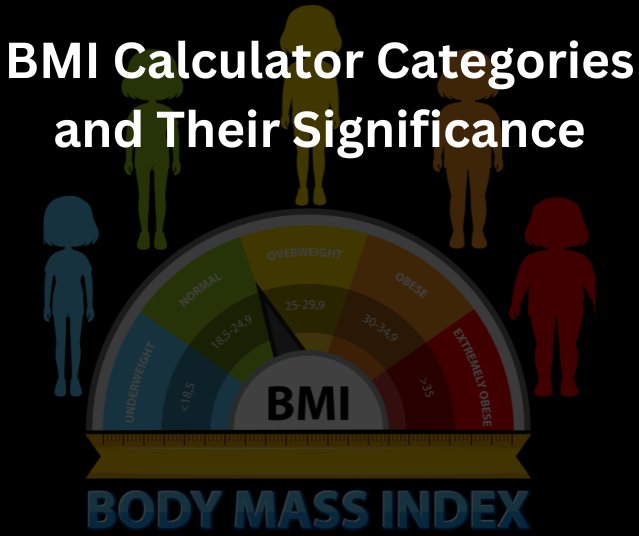
Underweight BMI Range
An underweight BMI is defined as less than 18.5. This may indicate nutritional deficiencies or underlying health issues that require attention.
Normal Weight BMI Range
A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered normal and typically associated with lower risks for chronic diseases.
Overweight and Obesity BMI Ranges
- Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9.
- Obesity: BMI of 30 or higher. Obesity is further categorized into three classes to better evaluate health risks.
Why Use a BMI Calculator?
BMI calculators are convenient and easy to use, making them a popular choice for individuals and healthcare professionals alike. They provide quick insights into your weight status and help identify potential health risks associated with being underweight or overweight.
Why BMI Calculator is Important
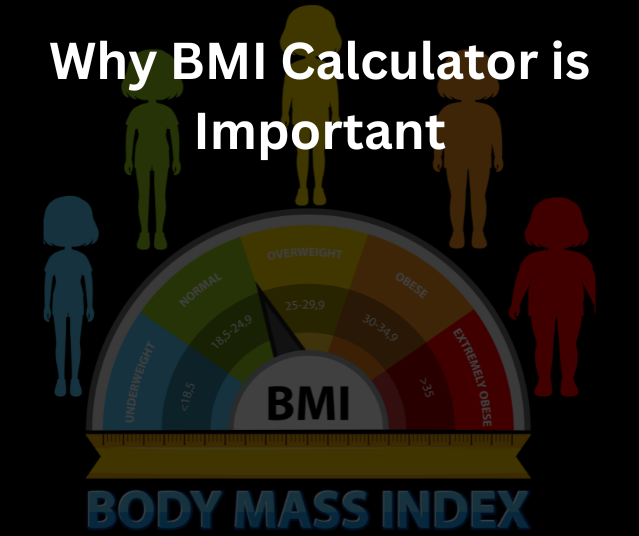
Evaluating Overall Health
BMI serves as a quick and easy screening tool for determining whether a person’s weight might lead to health complications.
Risk Assessment for Chronic Diseases
High or low BMI values can be linked to risks of conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and malnutrition. By knowing your BMI, you can take proactive steps to manage your health.
Limitations of BMI Calculator
Lack of Differentiation Between Fat and Muscle
BMI does not account for body composition. Athletes with high muscle mass might have a high BMI but low body fat.
Ignoring Other Health Metrics
BMI doesn’t consider factors like bone density, hydration levels, or fat distribution, which can provide a more nuanced picture of health.
BMI Calculator and Different Demographics
Age and BMI Calculator
Age significantly influences BMI and its interpretation. For instance, older adults may have a higher BMI due to muscle loss and fat redistribution, while children and teens require age-specific BMI charts to accurately assess their growth and health.
Gender Variations
Men and women often have different body compositions, with women generally having higher body fat percentages than men at the same BMI. This difference makes gender-specific considerations important when interpreting BMI.
Ethnic Considerations
Ethnicity can also affect BMI-related health risks. For example, some populations, such as South Asians, may experience higher risks for diabetes and cardiovascular diseases at lower BMI thresholds than other groups.
Alternatives to BMI Calculator
Body Fat Percentage
Body fat percentage directly measures the proportion of fat in your body, offering a more precise assessment of body composition compared to BMI.
Waist-to-Hip Ratio
This metric evaluates fat distribution, particularly around the abdominal area, which is a critical risk factor for metabolic diseases.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Methods like DEXA scans, CT scans, and MRIs provide comprehensive insights into body composition, though they are more costly and less accessible than BMI.
How to Improve Your BMI use of BMI Calculator
Diet and Nutrition
Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, is essential for achieving and maintaining a healthy BMI.
Physical Activity
Regular exercise, including aerobic activities and strength training, helps manage weight and improve overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Professional Guidance
Consulting healthcare professionals like dietitians or personal trainers can provide personalized strategies tailored to your body and goals.
The Role of BMI Calculator in Public Health
Population-Level Health Monitoring
BMI is a vital tool in public health for identifying trends in obesity and undernutrition across different populations, helping allocate resources where needed.
Informing Health Policies
Governments and organizations use BMI data to design and implement policies aimed at improving nutrition, promoting physical activity, and addressing health disparities.
Common Misconceptions About BMI Calculator
BMI Calculator as a Standalone Health Metric
BMI is often criticized for being oversimplified. While useful, it should not be used as the sole indicator of health. Combining BMI with other metrics provides a more comprehensive understanding of health.
Misunderstanding BMI Categories
Some individuals may misinterpret BMI categories. For example, a “normal” BMI does not always guarantee optimal health, nor does an “overweight” BMI automatically signify poor health.
Preparing to Calculate BMI by BMI Calculator
Information You’ll Need
To use a BMI calculator, you need two pieces of information:
- Your Weight: Typically measured in kilograms (kg) or pounds (lbs).
- Your Height: Measured in meters (m), centimeters (cm), or feet and inches.
Common Measurement Units
BMI calculators often let you choose your preferred measurement system:
- Metric System: Weight in kilograms and height in meters or centimeters.
- Imperial System: Weight in pounds and height in feet and inches.
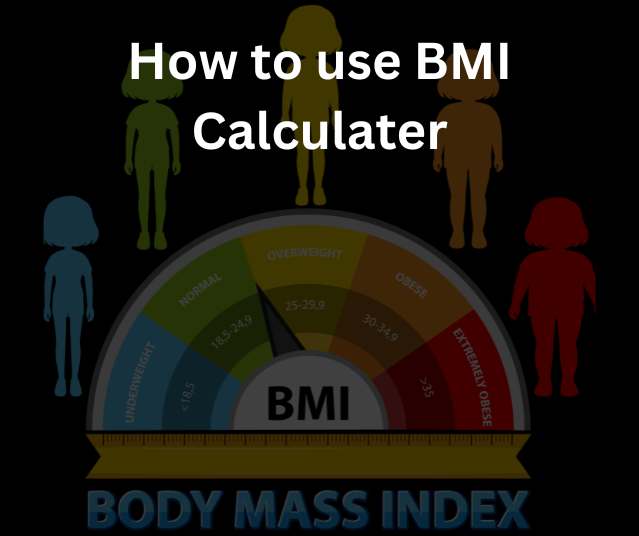
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a BMI Calculator
Step 1: Choose Your BMI Calculator
Find a reliable BMI calculator. Options include online calculators, smartphone apps, or even manual calculation using the BMI formula. Online tools are usually the most accessible and user-friendly.
Step 2: Enter Your Height and Weight
- Input your height and weight into the calculator.
- Select the appropriate units (metric or imperial).
- Double-check your entries to ensure accuracy.
Step 3: Interpret the Results
Once you input your data, the calculator will provide your BMI value. Alongside the number, most tools will display a category (e.g., normal weight, overweight) to help you understand your result.
Interpreting Your BMI Calculator Results
BMI Categories Explained
BMI results are divided into categories:
- Underweight: Less than 18.5
- Normal Weight: 18.5 to 24.9
- Overweight: 25 to 29.9
- Obese: 30 or higher
What Your BMI Calculator Tells You About Your Health
Your BMI offers a general idea of whether your weight is healthy. For example:
- A BMI in the normal range suggests lower risks for chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease.
- Higher BMI values may indicate risks for obesity-related health problems.
Tips for Accurate BMI Calculator
Measuring Weight Accurately
- Use a reliable scale on a flat, hard surface.
- Weigh yourself in the morning, before eating or drinking.
- Remove heavy clothing and shoes for a more accurate reading.
Measuring Height Correctly
- Stand straight against a wall without shoes.
- Use a measuring tape or height chart.
- Ensure the tape is level for the most accurate measurement.
Different Types of BMI Calculator
Online BMI Calculators
These are the most commonly used tools, accessible through websites. They provide quick results and often include additional resources to interpret your BMI.
BMI Apps for Smartphones
Mobile apps make tracking your BMI convenient. Some apps integrate with fitness trackers for a more comprehensive view of your health.
Manual Calculation of BMI Calculator
You can calculate your BMI manually using the formula:
BMI=Weight (kg)Height (m)2BMI = \frac{\text{Weight (kg)}}{\text{Height (m)}^2}BMI=Height (m)2Weight (kg)
Advantages and Limitations of BMI Calculator
Benefits of Using a BMI Calculator
- Speed: Instant results.
- Simplicity: Easy to use, even for beginners.
- Accessibility: Available online, offline, and via mobile apps.
Common Limitations to Keep in Mind
- BMI does not account for differences in muscle mass, bone density, or fat distribution.
- It may not be accurate for athletes, elderly individuals, or those with unique body compositions.
Alternative Tools for Assessing Health

Body Fat Calculators
These tools estimate your body fat percentage, offering a more detailed view of your body composition.
Waist-to-Hip Ratio Tools
This method measures the ratio of your waist circumference to your hip circumference, providing insights into fat distribution and related health risks.
Advanced Health Monitoring Methods
High-tech solutions like DEXA scans or bioelectrical impedance analysis provide precise data but may require professional facilities.
How to Improve Your BMI Score by BMI Calculator
Healthy Eating Habits
- Incorporate nutrient-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Avoid excessive sugar and processed foods.
Regular Physical Activity
- Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly.
- Combine aerobic activities with strength training for best results.
Tracking Progress Over Time
Monitor your BMI regularly to assess changes and adjust your lifestyle habits accordingly.
The Science Behind BMI Calculator : How It’s Calculated and Why It Matters
The BMI Categories
BMI is divided into categories that help determine whether a person’s weight is in a healthy range.
- Underweight
- BMI < 18.5
- May indicate insufficient nutrition or underlying health issues.
- Normal Weight
- BMI 18.5–24.9
- Generally considered a healthy weight range.
- Overweight
- BMI 25–29.9
- Associated with an increased risk of certain health conditions, like high blood pressure.
- Obesity
- BMI ≥ 30
- Often linked to chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease.
It’s important to note that these categories are generalized and may not account for individual differences in muscle mass, bone density, or other factors.
Why Does BMI Matter?
BMI is more than just a number; it’s a tool used by healthcare professionals to identify potential health risks.
- Health Risk Assessment
A high BMI is often associated with an increased risk of conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Conversely, a very low BMI may indicate malnutrition or other health concerns.
- Public Health and Research
BMI plays a crucial role in population studies, helping researchers identify trends in obesity, malnutrition, and related health outcomes.
- Easy and Accessible
BMI’s simplicity makes it a practical choice for both individuals and healthcare providers looking for a quick assessment of body weight.
Strengths of Using BMI Calculator
- Ease of Use: Requires only weight and height, making it quick to calculate.
- Cost-Effective: A simple tool for large-scale health screenings.
- Standardized Measurement: Provides a consistent way to compare health data across populations.
Limitations of BMI Calculator
Despite its usefulness, BMI has notable shortcomings:
- Doesn’t Differentiate Between Fat and Muscle: Athletes with high muscle mass may have a high BMI but low body fat.
- Varies by Age and Sex: Older adults may have a higher BMI due to reduced muscle mass, while women may naturally have higher fat percentages than men.
- Cultural Differences: Ethnic groups may have different body compositions, making standard BMI ranges less accurate for certain populations.
BMI vs. Other Health Metrics
While BMI is widely used, it’s not the only tool for assessing health. Here’s how it compares to other metrics:
- Waist-to-Hip Ratio (WHR)
- What It Measures: The ratio of waist circumference to hip circumference.
- Why It Matters: WHR provides insight into fat distribution, particularly abdominal fat, which is a higher risk factor for heart disease than overall body fat.
- Body Fat Percentage
- What It Measures: The proportion of fat mass to total body mass.
- Why It Matters: It offers a direct assessment of body composition, distinguishing fat from muscle. Tools like bioelectrical impedance scales or skinfold calipers are often used to measure this.
- Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
- What It Measures: The number of calories your body needs at rest to maintain basic functions like breathing and circulation.
- Why It Matters: BMR helps determine your overall energy needs and can guide weight management plans.
These tools, when used alongside BMI, provide a more comprehensive understanding of a person’s health and fitness levels.
The Science Behind BMI Calculator and Chronic Diseases
A key reason BMI is so widely used is its correlation with various chronic diseases. Here’s what the research says:
- Heart Disease
Higher BMIs are strongly linked to increased risk of cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension, coronary artery disease, and stroke. Excess fat, particularly around the abdomen, is a significant risk factor.
- Type 2 Diabetes
Studies consistently show that individuals with a BMI in the overweight or obese range are at a higher risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
- Low BMI Risks
While high BMI often garners more attention, being underweight (BMI < 18.5) is associated with risks like osteoporosis, weakened immunity, and fertility issues.
Interpreting BMI Calculator Across Cultures
The global use of BMI doesn’t always account for differences in body composition across populations.
- Asian Populations
Research shows that people of Asian descent may have higher health risks at lower BMI ranges due to differences in fat distribution. For example, a BMI of 23 may indicate overweight status in Asian populations, compared to 25 in Western populations.
- Ethnic Variations
Certain ethnic groups naturally have different muscle-to-fat ratios, which can skew BMI interpretations. African Americans, for instance, tend to have higher muscle mass, leading to slightly higher BMI readings without increased health risks.
- Adjustments in Guidelines
Organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) have recommended adjusted BMI cutoffs for certain populations to account for these differences.
BMI for Children and Adolescents
BMI isn’t just for adults—it’s also used to assess the health of children and teens, but the calculations and interpretations differ.
- Growth Charts and Percentiles
For children, BMI is plotted on growth charts that account for age and sex. Instead of fixed categories, percentiles are used:
- Underweight: Below the 5th percentile
- Healthy Weight: 5th to 85th percentile
- Overweight: 85th to 95th percentile
- Obese: Above the 95th percentile
- Importance of Monitoring
Tracking BMI in children can help identify early signs of undernutrition or obesity, allowing for timely interventions
How to Improve BMI Calculator Results
If your BMI falls outside the normal range, small lifestyle changes can help bring it closer to your health goals.
- Diet
- Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Reduce intake of processed foods and added sugars.
- Exercise
- Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, such as brisk walking or cycling.
- Incorporate strength training to build muscle and improve overall body composition.
- Consistency
Improving BMI isn’t about crash diets or extreme measures—it’s about sustainable habits that promote long-term health.
Myths About BMI Calculator
BMI is often misunderstood, leading to common myths that need debunking:
- “BMI Accurately Measures Fitness”
Not true—BMI doesn’t distinguish between fat and muscle. A bodybuilder with low fat could have a high BMI due to muscle mass.
- “Normal BMI Means Perfect Health”
While a normal BMI reduces certain health risks, it doesn’t guarantee overall fitness or the absence of underlying health issues.
- “BMI Is Useless”
Despite its limitations, BMI remains a valuable screening tool when used alongside other health metrics.
BMI and Mental Health
Beyond physical health, BMI can also impact mental well-being, often due to societal pressures and stigma.
- Psychological Impact
Individuals with high or low BMI may face judgment or discrimination, leading to stress, anxiety, or low self-esteem.
- Holistic Health Assessments
Healthcare providers are increasingly recognizing the need for a holistic approach that includes mental health alongside physical metrics like BMI.
- Promoting Body Positivity
Encouraging a focus on overall health rather than just weight fosters a more positive relationship with one’s body.
Watch Youtube Video For additional guidance:
Conclusion
BMI is a simple, widely-used tool for assessing body weight relative to height. While it offers valuable insights into health risks and trends, its limitations mean it should not be relied upon exclusively. For a more holistic understanding of your health, consider additional metrics like body fat percentage or waist-to-hip ratio, and seek professional advice when needed.
FAQs
Is BMI Calculator a reliable health indicator?
BMI is a useful screening tool, but it has limitations. It should be combined with other health assessments for a more accurate picture of overall health.
What is a healthy BMI?
A healthy BMI typically ranges from 18.5 to 24.9. However, this can vary based on individual factors like age, gender, and ethnicity.
How can I improve my BMI Calculator score?
Focus on maintaining a balanced diet, staying active, and seeking professional guidance to achieve a sustainable and healthy weight.
Are there better alternatives to BMI Calculator?
Yes, metrics like body fat percentage, waist-to-hip ratio, and advanced imaging techniques can offer more detailed insights into body composition.
Does BMI Calculator vary across age groups?
Absolutely. Children, teens, and older adults require age-specific BMI evaluations to account for developmental and age-related changes.










