Understanding how long it takes to digest food is essential for anyone interested in health and wellness. The process of digestion is complex, involving a series of mechanical and chemical actions that break down food into nutrients the body can absorb. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of the digestive system and examine the factors that affect digestion time. We will also answer the primary question: how long does it take to digest food ?
What Is Digestion?
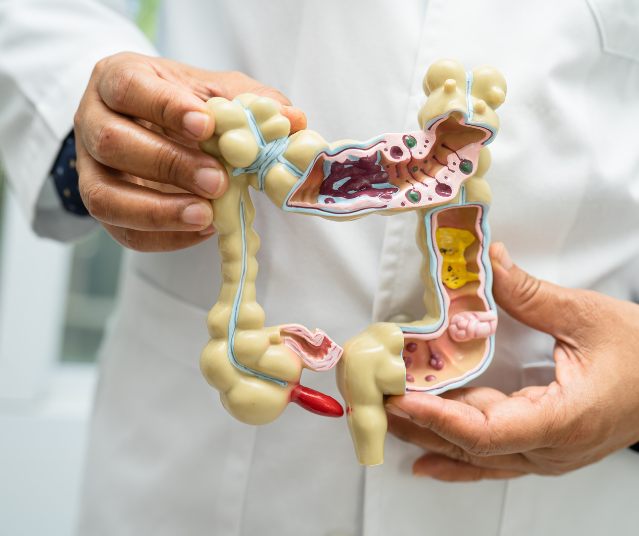
Digestion is the process through which the body breaks down food into nutrients that can be absorbed and used for energy, growth, and cell repair. The journey of digestion begins in the mouth and continues through the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine, with each stage contributing to breaking down and absorbing nutrients. how long does it take to digest food ? The answer varies depending on the type of food consumed, individual metabolism, and other factors.
The process begins in the mouth, where chewing and enzymes in saliva start breaking down food, particularly carbohydrates. From there, food moves down the esophagus into the stomach, where it is mixed with stomach acids and enzymes to break down proteins and further liquefy the food. This stage typically takes around 2 to 4 hours, depending on the meal’s complexity.
Next, the food passes into the small intestine, where most nutrient absorption occurs. Bile from the liver and digestive enzymes from the pancreas aid in digesting fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. The small intestine absorbs nutrients into the bloodstream over 3 to 6 hours.
Finally, undigested food and waste move into the large intestine, where water and minerals are absorbed, and the remaining material is processed into stool. This stage can take anywhere from 24 to 48 hours, meaning that total digestion time for a meal ranges widely, from about 24 hours to several days.
Factors like fiber content, fat levels, and individual digestive health can all affect how long it takes to digest food. Foods rich in fiber, for example, tend to move more quickly through the digestive tract, while fatty foods take longer to digest. Understanding digestion helps individuals make better dietary choices for optimal health and comfort.
How Long Does It Take to Digest Food ?
The question “how long does it take to digest food ?” does not have a straightforward answer. Several factors influence the digestion timeline, including:
- Type of Food: Carbohydrates generally digest faster than proteins and fats. For example, fruits and vegetables can take as little as 30 minutes to digest, while heavy meals with high fat can take 4-6 hours or more.
- Meal Size: Larger meals take longer to digest than smaller ones. A big feast can extend digestion time significantly.
- Individual Factors: Age, metabolism, and overall health can all affect digestion speed. Younger individuals often have faster digestion rates compared to older adults.
The Science Behind Digestion Timing
The process of digestion is highly complex and involves both mechanical and chemical mechanisms that break down food and convert it into nutrients that the body can absorb and use. Here’s an in-depth look into the science behind digestion timing and the approximate time it takes to digest various types of food.
Overview of Digestion
Digestion begins as soon as you start chewing food and continues through the entire digestive tract until waste is excreted from the body. The process involves several organs, including the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and accessory organs like the liver and pancreas. If you’re wondering how long does it take to digest food, this process can vary depending on the type of food, but generally, it takes anywhere from 24 to 72 hours for food to fully digest and pass through your system.
The timing of digestion can vary greatly depending on factors like the type of food eaten, individual metabolism, health conditions, and age. Digestion timing is important because it influences energy levels, nutrient absorption, and even overall gut health.
Stages of Digestion and Approximate Timing

- Mouth (Chewing and Saliva Enzymes)
- Time: A few seconds to a minute.
- Process: Digestion begins in the mouth, where chewing mechanically breaks down food into smaller pieces. Salivary enzymes, particularly amylase, start breaking down carbohydrates.
- Esophagus (Swallowing and Transport)
- Time: 1-2 seconds.
- Process: Food is pushed down the esophagus via peristalsis, a wave-like muscle contraction, which delivers food to the stomach.
- Stomach (Mechanical and Chemical Breakdown)
- Time: 2-6 hours, depending on food type.
- Process: Food enters the stomach, where it’s mixed with stomach acid and digestive enzymes. This acidic environment is ideal for breaking down proteins and continuing carbohydrate digestion. The stomach also churns food, turning it into a semi-liquid substance called chyme.
- Timing for Different Foods in the Stomach:
- Carbohydrates: 2-3 hours.
- Proteins: 3-4 hours.
- Fats: 4-6 hours or longer.
- Small Intestine (Absorption and Enzyme Activity)
- Time: 3-6 hours.
- Process: The chyme moves into the small intestine, where most nutrient absorption occurs. The pancreas releases digestive enzymes (lipase, protease, amylase) that further break down fats, proteins, and carbohydrates, while bile from the liver emulsifies fats for absorption. Nutrients are absorbed through the intestinal walls and enter the bloodstream.
- Large Intestine (Water Absorption and Waste Formation)
- Time: 10-48 hours.
- Process: Any undigested food enters the large intestine, where water is reabsorbed, and bacteria help break down remaining material. This process forms stool, which is eventually excreted. The bacteria also produce certain vitamins and gases as byproducts of digestion.
Digestion Timing for Common Foods
- Fruits (Apples, Bananas, Berries): 30 minutes to 1 hour.
- Vegetables (Leafy Greens, Cucumbers): 1-2 hours.
- Grains (Rice, Pasta, Bread): 2-3 hours.
- Dairy (Milk, Cheese): 2-3 hours.
- Proteins (Chicken, Beef, Fish): 3-4 hours.
- High-Fat Foods (Nuts, Oils): 4-6 hours.
Importance of Digestion Timing
Understanding how long it takes to digest food is crucial for optimizing meal timing and energy management. For example:
- Exercise: Waiting 2-3 hours after a large meal allows enough time for digestion to prevent discomfort.
- Weight Management: Eating foods with slower digestion, like fiber-rich vegetables and whole grains, helps keep you feeling full for longer and may support weight management.
- Sleep Quality: Eating heavy or fatty foods late at night can disrupt sleep due to slower digestion during rest.
The Role of Enzymes
Digestive enzymes are crucial in breaking down food. Each type of food requires specific enzymes for digestion:
- Carbohydrates: Amylase is an enzyme that starts breaking down carbohydrates in the mouth and continues in the small intestine.
- Proteins: Proteases are enzymes that break down proteins into amino acids. This process starts in the stomach.
- Fats: Lipases are responsible for breaking down fats. This occurs primarily in the small intestine, aided by bile from the liver.
These enzymes work efficiently, but their effectiveness can vary based on the individual and the food type.
Factors Influencing Digestive Timing
how long does it take to digest food ? Digestion timing is a complex process influenced by several factors, each of which can speed up or slow down how long it takes to break down food and absorb nutrients. In this breakdown, we’ll cover these key elements in detail.
1. Type of Food Consumed
Different food types take varying amounts of time to digest due to their composition:
- Carbohydrates (e.g., fruits, vegetables, grains) are typically digested faster than proteins and fats, taking around 1-4 hours.
- Proteins (e.g., meat, dairy, legumes) take longer, often requiring 4-6 hours.
- Fats (e.g., oils, nuts, fatty meats) take the longest, up to 8 hours or more. So, how long does it take to digest food depends greatly on its type.
2. Meal Composition and Size
- Larger meals usually take longer to digest than smaller meals due to the greater quantity of food that must be processed.
- Mixed meals (containing carbs, fats, and proteins) require more time to digest than meals with a single macronutrient, as the stomach and intestines work to break down each component differently. This can impact how long does it take to digest food after eating a mixed meal.
3. Hydration Levels
- Proper hydration aids in breaking down food and moving it through the digestive tract. Water intake before, during, and after meals can impact how long does it take to digest food by keeping the digestive system lubricated and aiding in waste elimination.
4. Individual Metabolism
- Each person’s metabolic rate affects how long does it take to digest food. People with faster metabolisms tend to process food quicker, while slower metabolisms may lead to more extended digestion periods. Age, body composition, and overall health are primary factors in determining an individual’s metabolic rate.
5. Digestive Health and Enzymatic Function
- Healthy enzyme production is essential for breaking down food. Those with insufficient enzyme production may experience delayed digestion, extending how long does it take to digest food. Conditions like lactose intolerance or enzyme deficiencies can significantly alter digestive timing.
6. Physical Activity Level
- Physical activity can boost metabolism and aid the movement of food through the digestive tract. Regular exercise may reduce how long does it take to digest food, while a sedentary lifestyle can slow down digestion and contribute to constipation or indigestion.
7. Stress and Emotional State
- Stress can negatively impact digestion by altering the release of digestive enzymes and hormones. Under stress, the “fight or flight” response can delay how long does it take to digest food, as blood flow is redirected away from the digestive organs to prepare for a physical response.
8. Time of Day
- Digestion tends to slow down at night, meaning a meal eaten before bedtime may take longer to digest than one eaten earlier. Therefore, how long does it take to digest food can be affected by the time it is consumed. Some experts recommend lighter meals in the evening to avoid overnight digestive strain.
9. Gut Microbiome Health
- The balance of bacteria in the gut plays a role in digestion. A healthy microbiome supports efficient digestion, potentially reducing how long does it take to digest food. An imbalance, however, can lead to slower digestion and bloating.
10. Hormones and Health Conditions
- Hormones such as insulin and cortisol can influence digestive timing. Additionally, health conditions like diabetes, thyroid disorders, and gastrointestinal diseases (e.g., IBS) can alter how long does it take to digest food. Hormonal changes and health issues can disrupt normal digestion and slow down or speed up food processing.
Each of these factors contributes uniquely to the overall question: how long does it take to digest food? While general estimates exist, understanding these variables is key to recognizing why digestion time varies so widely between individuals. For the average person, it may take anywhere from 6 to 8 hours for food to pass through the stomach and small intestine, with the total journey through the digestive tract extending up to 30 hours or more. However, with a mindful approach to diet, hydration, and lifestyle, one can influence how long does it take to digest food and potentially improve digestive health overall.
Read More : Belly Fat Exercises
Typical Digestive Timing for Common Foods
Understanding the general timing of digestion can give insight into how these factors play out:
- Liquids (water, clear juices): 20-30 minutes
- Fruits and Vegetables (high in water and fiber): 30 minutes to 2 hours
- Grains and Complex Carbohydrates (rice, pasta, potatoes): 2-3 hours
- Proteins (chicken, beef, fish): 3-4 hours
- Fats (oils, fried foods): 6 hours or more
Ultimately, these factors combine to affect how long food takes to digest, which can vary widely based on individual circumstances and lifestyle choices.
How to Support Healthy Digestion
Supporting healthy digestion is crucial for overall wellness, and understanding how long does it take to digest food can guide you in making better choices for your digestive health. The process of digestion is complex, involving various organs and enzymes that work together to break down food, absorb nutrients, and eliminate waste. Let’s dive into ways to support healthy digestion and answer the question, how long does it take to digest food?
1. Eat a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats can greatly enhance digestion. Fiber is especially essential because it helps food move through the digestive tract more smoothly, which can impact how long does it take to digest food. Soluble fiber, found in oats, apples, and beans, absorbs water and softens stool, while insoluble fiber from whole grains and vegetables adds bulk, speeding up the digestive process.
2. Stay Hydrated
Hydration is essential for digestion, as water aids in breaking down food and absorbing nutrients. Without adequate water, digestion slows down, potentially affecting how long does it take to digest food. Drinking water between meals helps prevent dehydration, which can lead to constipation and other digestive issues. Additionally, water helps your body produce digestive enzymes that further break down food.
3. Manage Stress
Stress can significantly impact digestion, slowing down or disrupting the process and thus affecting how long does it take to digest food. High levels of stress can trigger digestive discomfort and symptoms like bloating or indigestion. Practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and regular exercise can help reduce stress, promoting smoother and faster digestion.
4. Avoid Overeating
Eating too much food in one sitting can overwhelm your digestive system, making it difficult to efficiently process food and impacting how long does it take to digest food. Large meals require more digestive enzymes and time to break down, often leading to bloating and indigestion. Eating smaller, more frequent meals allows your body to digest food more comfortably and steadily.
5. Chew Food Thoroughly
Proper chewing initiates the digestive process by breaking down food how long does it take to digest food into smaller particles and mixing it with saliva, which contains enzymes that start carbohydrate digestion. Chewing food well makes it easier for the stomach and intestines to process, ultimately affecting how long does it take to digest food. Aim to chew each bite thoroughly to support more efficient digestion.
How Long Does It Take to Digest Food ?
So, how long does it take to digest food? Generally, digestion can take anywhere from six to eight hours for food to pass through the stomach and small intestine. However, it may take up to 72 hours for the complete digestion and elimination process, depending on factors like the type of food eaten, individual metabolic rate, and overall digestive health.
Different types of food digest at different rates. Carbohydrates tend to digest the quickest, often in one to two hours. Proteins take longer, and fats can take the longest, up to four hours. Understanding how long does it take to digest food helps in planning balanced meals and snack times to keep digestion running smoothly.
Supporting healthy digestion involves a combination of dietary habits, hydration, stress management, and mindful eating. By focusing on these aspects, you can improve the efficiency of your digestive system and have a better grasp of how long does it take to digest food in various situations.
Know More : Digestive System
Conclusion
In conclusion, the answer to the question how long does it take to digest food? varies based on numerous factors, including the type of food, meal size, and individual health. Generally, the digestive process can take anywhere from a few hours to a couple of days. By understanding the workings of the digestive system and adopting habits that support healthy digestion, you can optimize this essential process.
The importance of digestion cannot be overstated, as it plays a vital role in overall health and well-being. With the right knowledge and practices, you can ensure your digestive system functions at its best, allowing you to enjoy the benefits of a well-balanced diet and a healthier lifestyle.










